Organic, sinuous lines, with vines snaking around stylized letters, ethereal women with flowing tresses, and botanical borders characterize the style of Art Nouveau, the enduringly popular movement that to this day adorns drawings, posters, notebook covers, and even tarot card decks. But where does the style come from and why is it still so enduringly popular today?
The answer can be found In the new exhibition, “Alphonse Mucha: Spirit of Art Nouveau,” on view through September 22 at the Art Gallery of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia. Billed as one of the most comprehensive presentations of Mucha’s art to date, the show features more than 200 works from drawings and photography to lithographs, sculptures, and paintings drawn from the Mucha Family Collection through the Mucha Foundation in Prague.
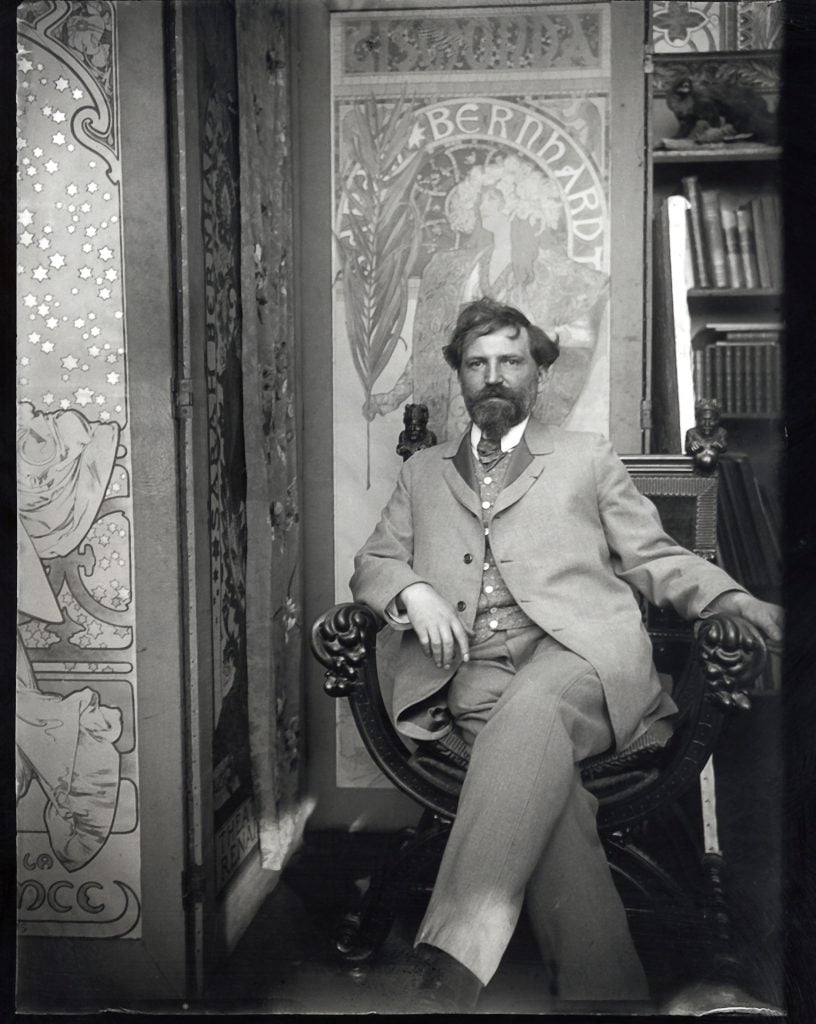

Self-portrait with posters for Sarah Bernhardt at Mucha’s studio in rue du Val-de-Grâce, Paris, c1901 © Mucha Trust 2024
Born in 1860 in Ivančice in South Moravia in today’s Czech Republic, the Czech artist rose to fame at the turn of the 20th century in his adopted home in Paris, where he arrived in 1887 as a student at the Académe Julian. He began working as an illustrator in 1889 for publishers in Paris and Prague, while dapping into designing posters, stage, and costumes.
In 1895, Mucha’s poster for the play Gismonda starring celebrated French actress Sarah Bernhardt brought him instant stardom. Bernhardt reportedly loved the poster and exclaimed: “Monsieur Mucha, you have made me immortal.”

Alphonse Mucha, Gismonda (1894) colour lithograph, 216 x 74.2 cm © Mucha Trust 2024.
The work made Mucha immortal, too. The distinctive drawing style and shape of the work was hailed as the birth of “Style Mucha,” characterized by the tendril-like lines and soft pastel colors. “The purpose of my work was never to destroy but always to create, to construct bridges,” he once said. The invention of a new visual language seen in his Art Nouveau posters, illustrations, and decorative panels, made Mucha a central figure of the art movement.
Throughout his eventful life, Mucha encountered many other key cultural figures at the time. He was friends with Paul Gauguin, with whom he said a studio, and Swedish playwright August Strindberg, with whom he practiced occult ceremonies. He also journeyed to the U.S., taught at the Art Institute of Chicago until 1909 before returning to his home country and started working on his The Slav Epic project.
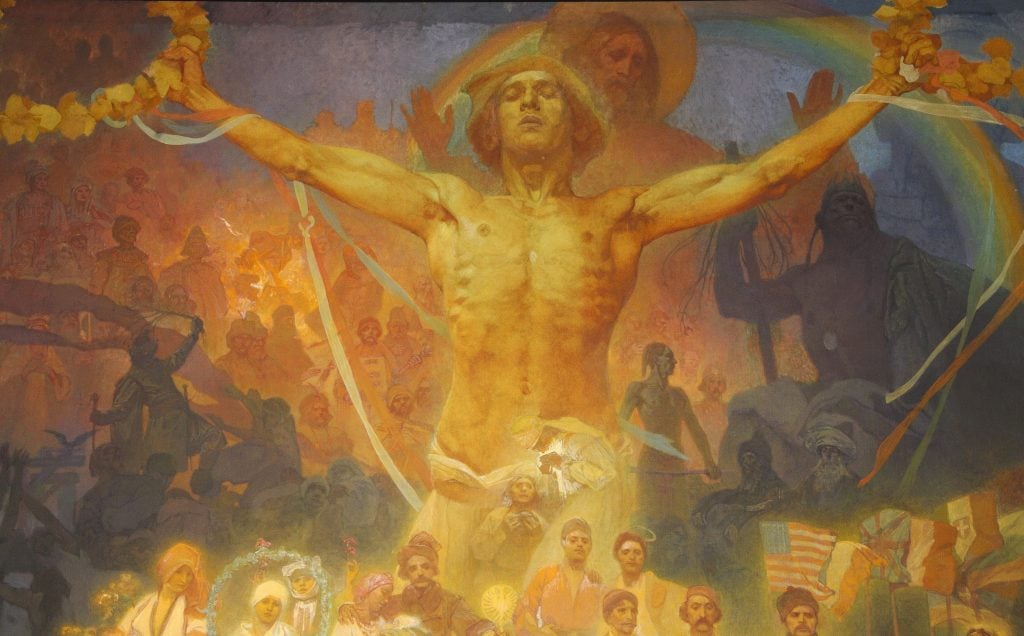

Alphonse Mucha, The Slav Epic XX: Apotheosis Slavs for Humanity (1926) (detail) egg tempera and oil on canvas, 480 x 405 cm © Mucha Trust 2024
Considered to be the most important work by Mucha, The Slav Epic consists of a series of 20 monumental canvases measured by 19 feet x 26 feet depicting the history and civilization of the Slav people. From conceiving the idea in 1899 to its final completion in 1926, Mucha dedicated his career to the project, which was a symbol of his devotion to the culture and his people. The series was gifted to the nation in 1928 to celebrate the 10th anniversary of Czechoslovakia’s independence from the Austria-Hungary Empire.
In 1939, he was arrested and interrogated by the Gestapo over his alleged Masonic and Slavic nationalist activities when Germany invaded Czechoslovakia. He was released but died shortly afterwards.
More images from the exhibition below.
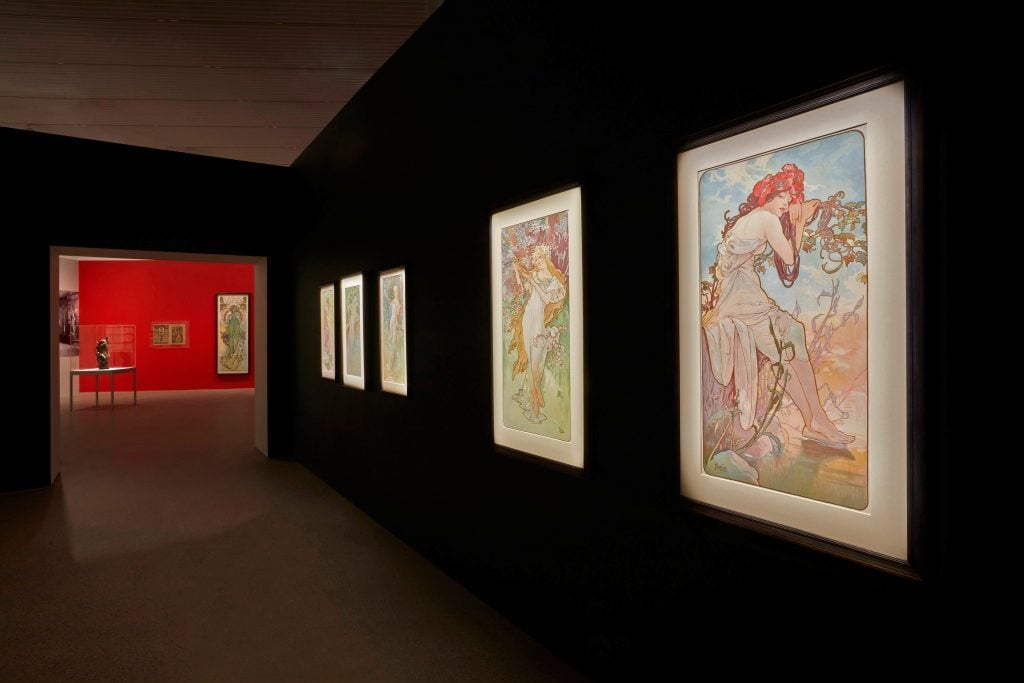

Installation view of the “Alphonse Mucha: Spirit of Art Nouveau” exhibition at the Art Gallery of New South Wales, 15 June 22 September 2024, photo © Art Gallery of New South Wales, Diana Panuccio

Alphonse Mucha, The Seasons: Summer (1896), color lithograph, 103 x 54 cm © Mucha Trust 2024.
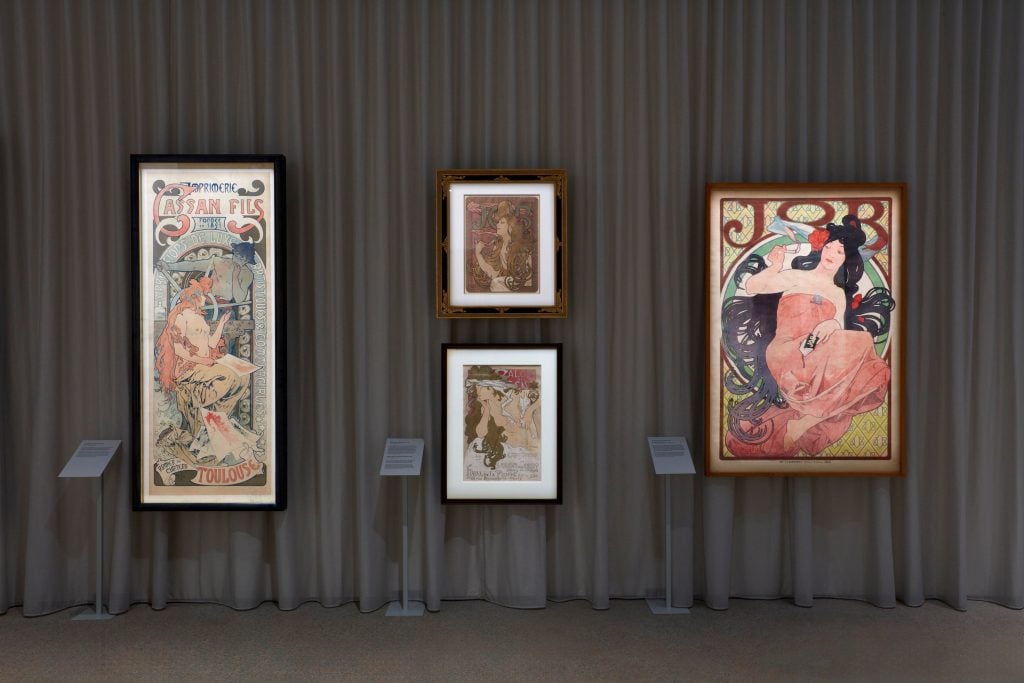

Installation view of the “Alphonse Mucha: Spirit of Art Nouveau” exhibition at the Art Gallery of New South Wales, 15 June 22 September 2024, photo © Art Gallery of New South Wales, Diana Panuccio

Alphonse Mucha, Poster for JOB cigarette papers (1896), colour lithograph, 66.7 x 46.4 cm © Mucha Trust 2024
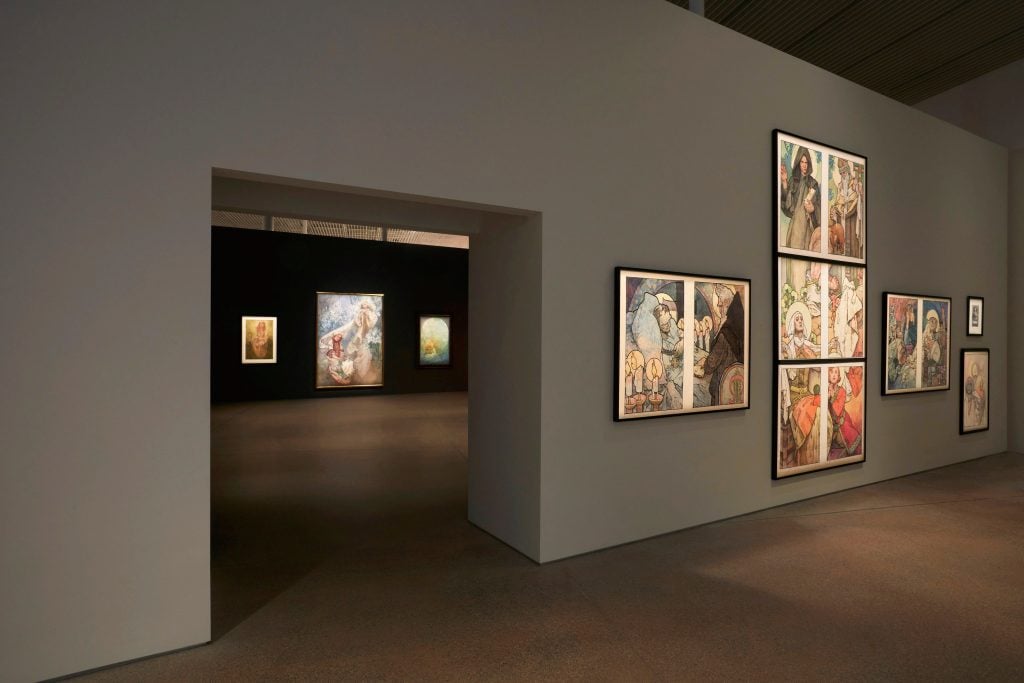

Installation view of the “Alphonse Mucha: Spirit of Art Nouveau” exhibition at the Art Gallery of New South Wales, 15 June 22 September 2024, photo © Art Gallery of New South Wales, Diana Panuccio

Alphonse Mucha, Reverie (1898), color lithograph, 72.7 x 55.2 cm © Mucha Trust 2024

Alphonse Mucha, Princess Hyacinth (1911), color lithograph 125.5 x 83.5 cm © Mucha Trust 2024
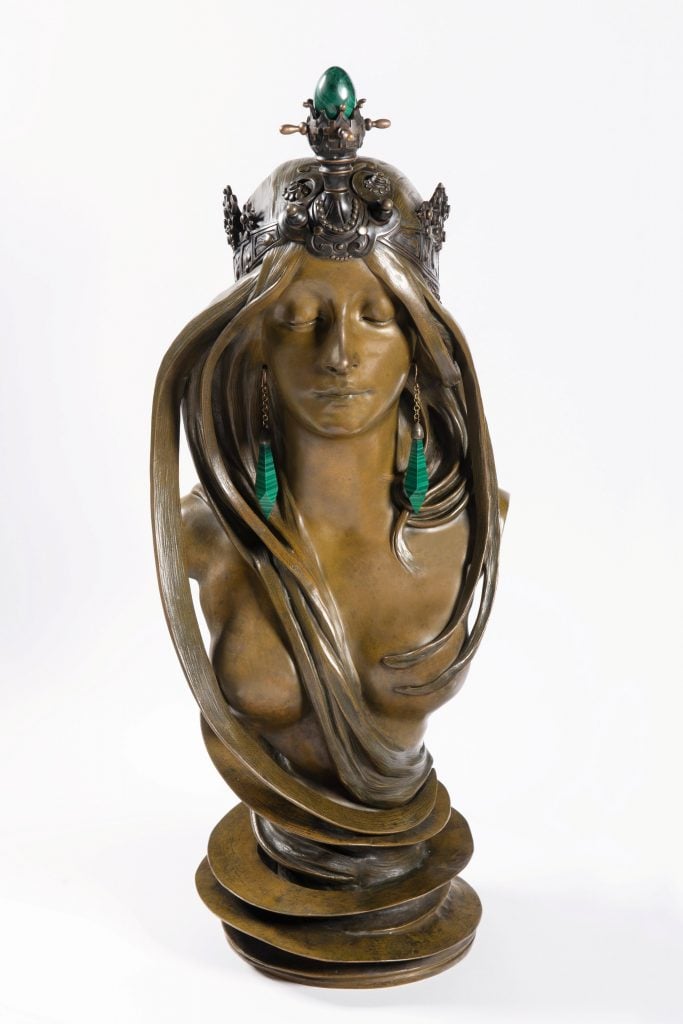

Alphonse Mucha, La Naturec1900, patinated bronze and malachite, 70 x 27 x 28 cm © Mucha Trust 2024

Alphonse Mucha, Poster for Slavia Mutual Saving Bank, Prague (1907), color lithograph, 54 x 36 cm © Mucha Trust
Follow Artnet News on Facebook:
References: this article is based on content originally published by Vivienne Chow on Artnet. You can read the full article here.