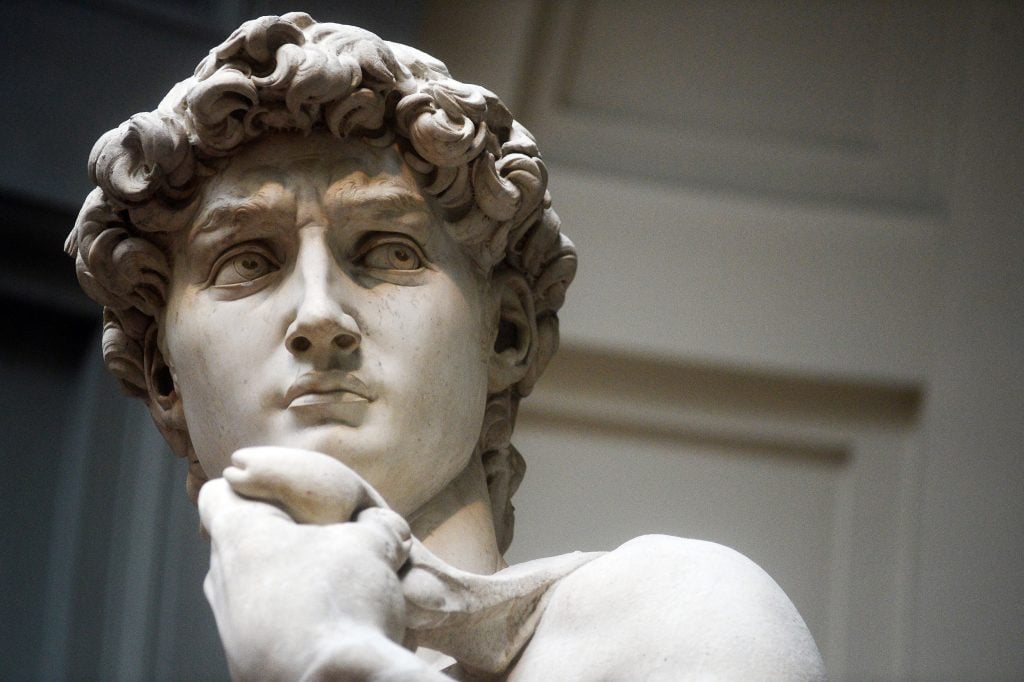
Michelangelo’s David was recognized as a masterpiece the moment it was unveiled. In fact, its commissioners found the sculpture so beautiful, and so massive, that they decided its intended home, high up in the roof of a cathedral, just wouldn’t cut it.
The statue was conceived almost a century before Michelangelo picked up a chisel to create it. In the early 1400s, the Opera del Duomo, the workshop of Florence’s cathedral, began commissioning pieces for a series of 12 massive sculptures depicting prophets from the Old Testament. These would each be housed in niches of the church’s tribune, semi-domed apses in the roofline, over 260 feet high.
In 1464, Agostino di Duccio, a sculptor inexperienced with projects at such a large scale, was commissioned to create the statue. Duccio traveled to a Carrara marble quarry in Tuscany, where he handpicked a giant block of stone. Upon its arrival in Florence after a long, arduous journey, the block was found to be a flop. The hewed hunk of marble was tall but thin and riddled with holes and veins, imperfections both unaesthetic and potentially compromising to the structure of so large a statue.
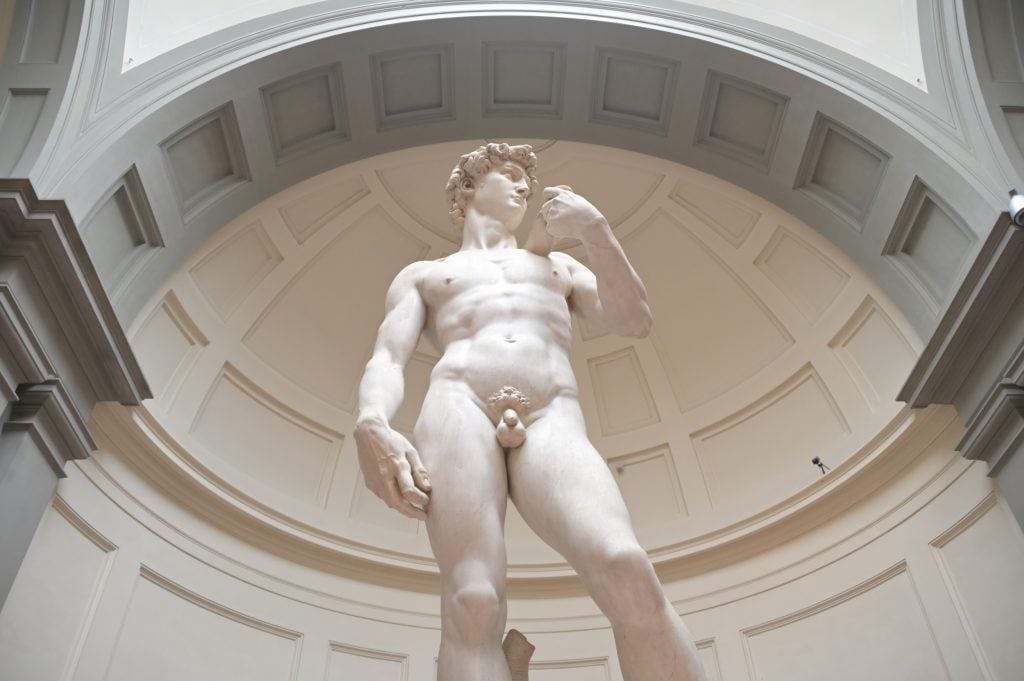

Michelangelo, David at the Galleria dell’Accademia in Florence. Photo by Paolo Lo Debole/Getty Images.
Realizing his error, Duccio chipped at the stone with his hammers and chisels for a while, but soon gave up on his work. The abandoned wedge of marble went untouched for a decade until another sculptor, Antonio Rossellino, seized the mantle. After some attempts to salvage the work, he, too, deemed the block unusable. It was left naked in the Opera’s courtyard for another 25 years.
Finally, in the summer of 1501, the workshop’s overseers assigned the work to Michelangelo. In just over two years, he transformed the misunderstood marble block into the 17-foot-tall statue that is today one of the most famous artworks in history. At the unveiling, the unexpected size, weight, and beauty of the statue demanded a reshuffling of plans. In 1504, 30 Florentine cultural leaders, including Leonardo da Vinci and Sandro Botticelli, convened to determine David’s fate.
After months of raging debate, it was decided that the statue deserved a spot in the Piazza della Signoria, in front of Florence’s town hall. It took 40 men four days to transport a rope-bound David, caged in wooden scaffolding, from Michelangelo’s workshop to the plaza a half-mile away. Upon arrival, the artist took his chisel to his creation one last time, applying finishing touches. The statue had been designed for viewing from far below; this unexpected setting and perspective required slight modifications.
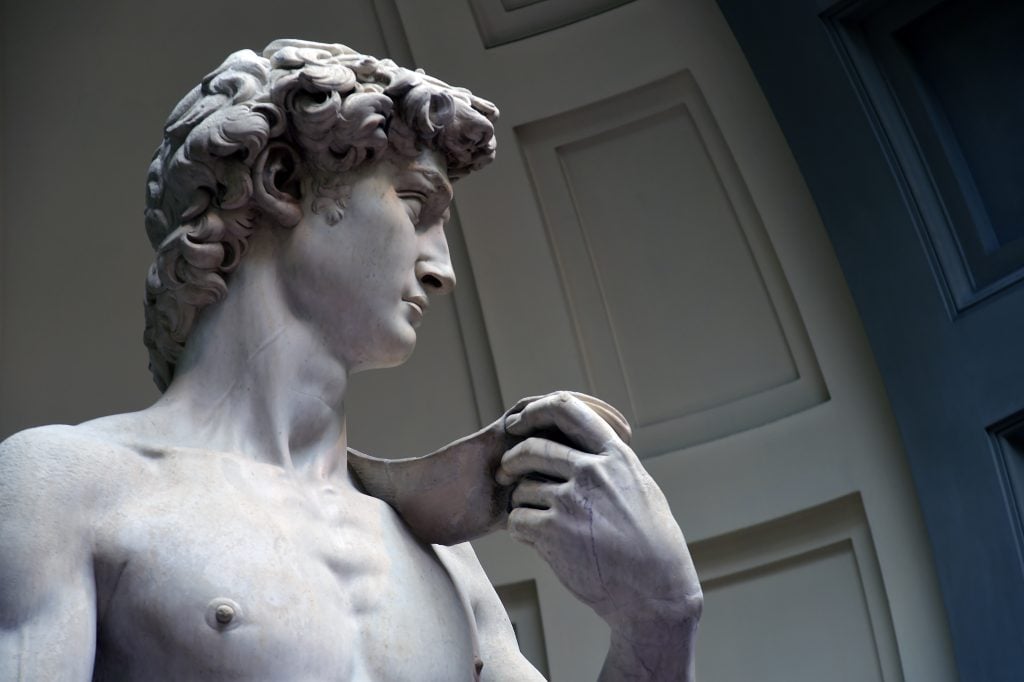

Michelangelo, David at the Galleria dell’Accademia in Florence. Photo: Roberto Serra, Iguana Press/Getty Images.
The statue became quickly known as “the Giant,” a symbol of liberty for the Florentine people, with his glare pointed at their rival city, Rome. Though beloved, the Giant fell victim to vandalism in his first year, when protestors pelted the colossal sculpture with stones. In 1527, a riot against the ruling class broke out in the plaza, and a bench thrown out of a window struck the statue, breaking its arm into three pieces. David went on to survive earthquakes and lightning strikes before the city council decided to protect him.
After almost 370 years, fans and art connoisseurs finally compelled the city to move David into the Galleria dell’Accademia for his protection in 1873; he still stands there today. Even in the confines of the museum, though, David was unsafe. In 1991, a mentally disturbed Italian artist, Pierro Cannata, snuck a hammer into the museum. With it, he lunged at David’s left foot, shattering a toe before being subdued by museum-goers. Cannata claimed that La Bella Nani, a figure from a Veronese painting, compelled him to strike David. Thanks to the attack, David’s beauty is now shielded from jealous hands and hammers by a wall of plexiglass.
What’s the deal with Leonardo’s harpsichord-viola? Why were Impressionists obsessed with the color purple? Art Bites brings you a surprising fact, lesser-known anecdote, or curious event from art history.
Follow Artnet News on Facebook:
References: this article is based on content originally published by on Artnet. You can read the full article here.