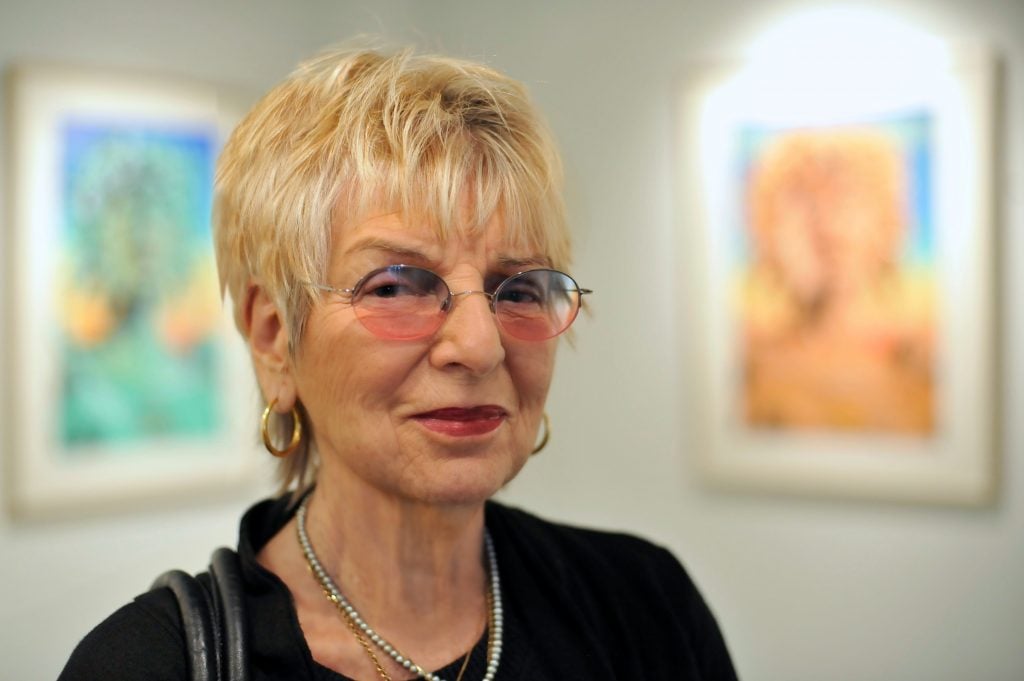
Feminist painter and sculptor Audrey Flack, one of the founders of Photorealism, died in Southampton, New York, on June 28. The 93-year-old artist’s death was confirmed by her former dealer and longtime friend, Louis K. Meisel.
Born in New York in 1931, Flack studied at the city’s Cooper Union before receiving a scholarship to Connecticut’s Yale School of Art, where she had been recruited by Josef Albers, the educator and painter of geometric abstraction.
As a young artist, Flack was immersed in the downtown New York art scene, rubbing elbows with the famed Abstract Expressionists Jackson Pollock—whose advances she rebuffed—and Willem de Kooning at the 8th Street Club and Cedar Tavern. But she carved out a space of her own at the forefront of Photorealism in the 1960s after additional studies at New York’s Art Students League.
“Audrey Flack’s contribution to the history of art cannot be overstated,” Hollis Taggart, the artist’s gallerist, told Art and Object earlier this year. “Audrey has consistently been at the forefront of challenging the artistic trends of her time.”
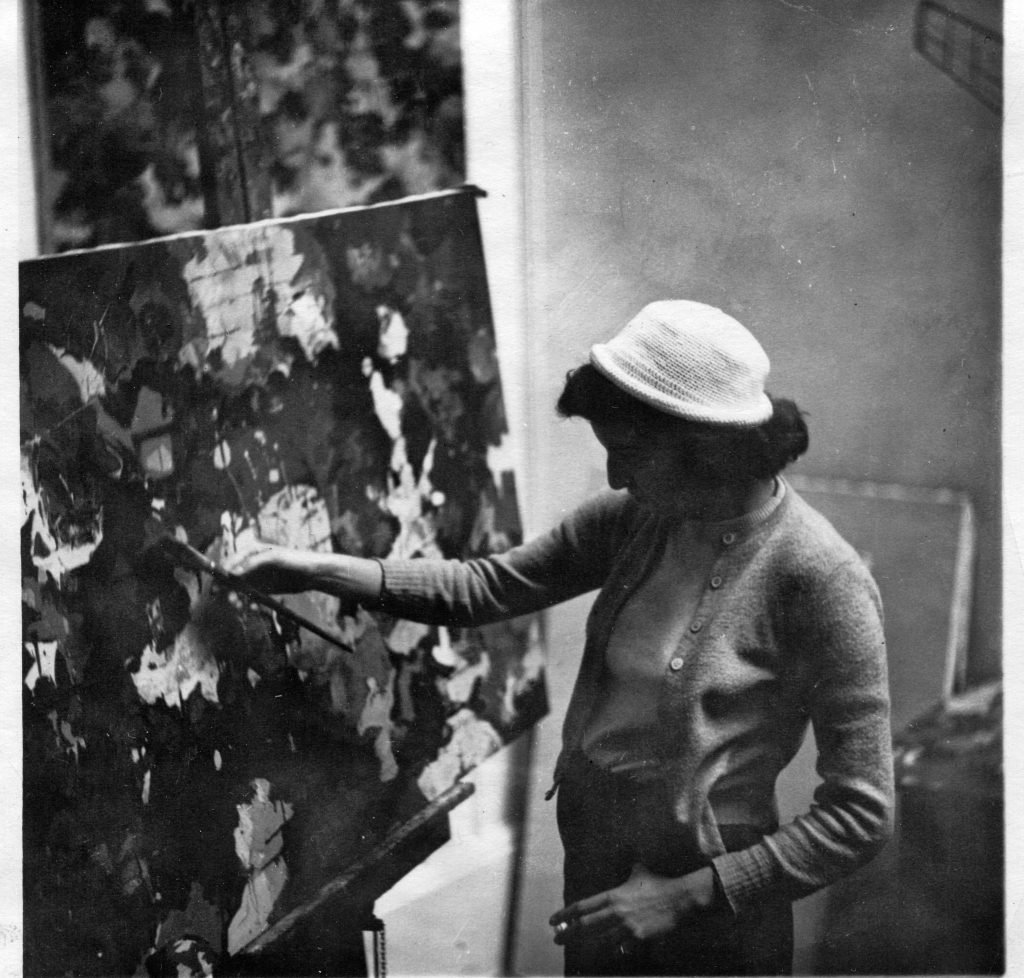

Audrey Flack painting at Yale University. Courtesy of the artist and Penn State University Press.
Painting from her own photographs, Flack created over-size still life paintings that often focused on feminine personal effects such as jewelry, makeup, and glassware, as well as religious artifacts.
“I broke the unwritten code of acceptable subject matter,” Flack wrote in an artist statement for the Brooklyn Museum. “Photorealists painted cars, motorcycles, and empty street scenes. Cool, unemotional, and banal were the terms used to describe the movement. My work, however, was humanist, emotional, and filled with referential symbolic imagery.”
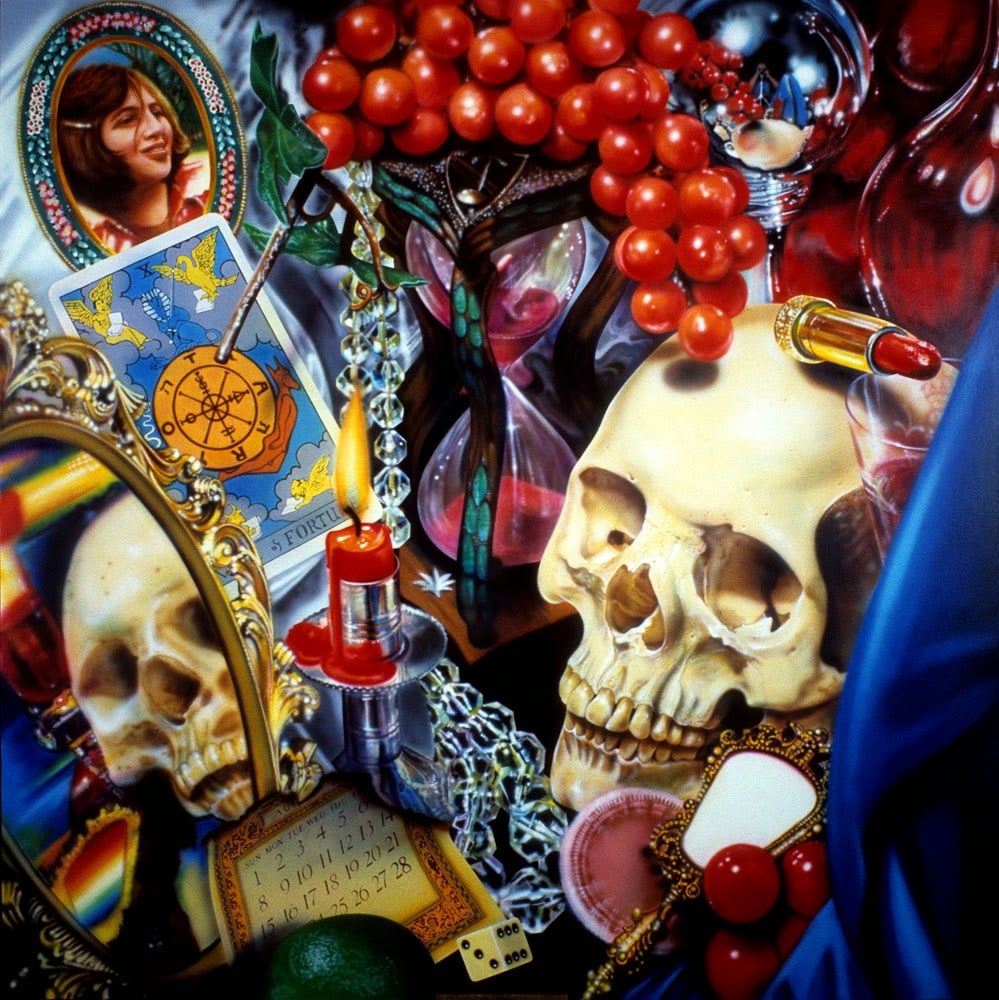

Audrey Flack, Wheel of Fortune (1977–78). Courtesy of Parrish Art Museum, Water Mill, New York, gift of Louis K. and Susan P. Meisel.
Some critics initially took umbrage with the elevation of such subject matter. In a review for the New York Times in 1976, Hilton Kramer called Flack “the Barbra Streisand of photorealism,” bemoaning that she was the first artist of the movement to have work purchased by New York’s Museum of Modern Art.
But with a career that ultimately stretched across seven decades, Flack’s groundbreaking approach was able to stand the test of time. That MoMA acquisition, Leonardo’s Lady, was prominently displayed when the expanded museum reopened in 2019.
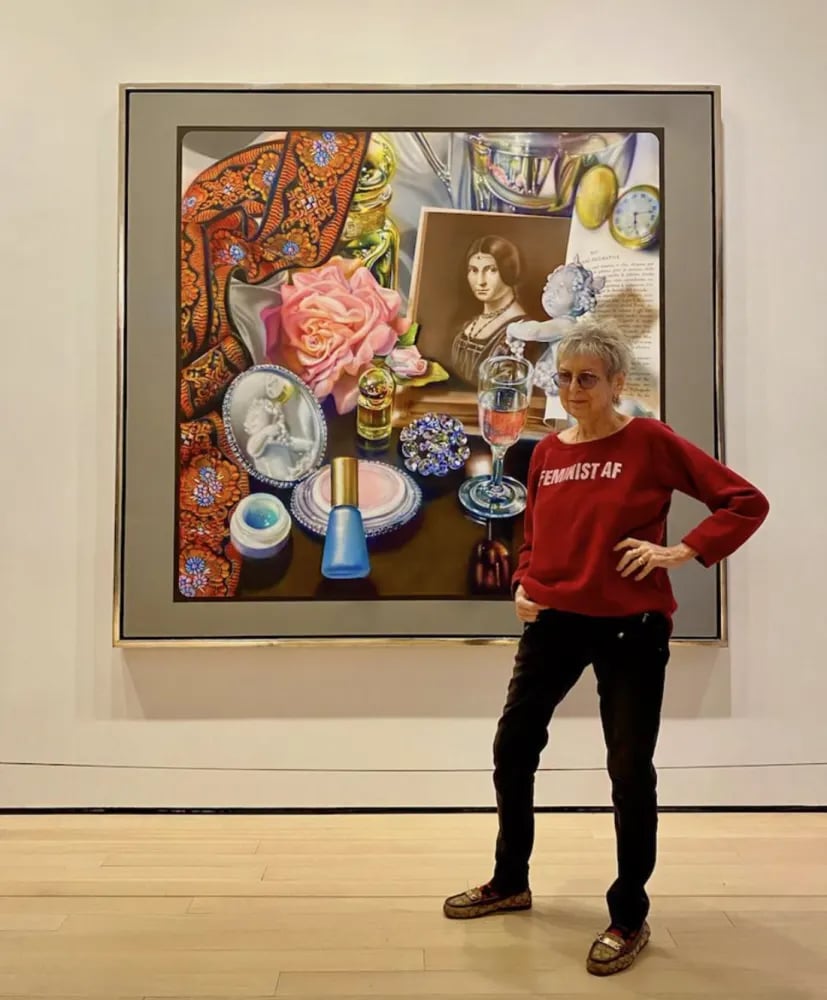

Audrey Flack with her painting Leonardo’s Lady at New York’s Museum of Modern Art in 2019. Photo courtesy of Hollis Taggart, New York.
She is also represented in the collections of New York’s Metropolitan Museum of Art, Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, and Whitney Museum of American Art, as well as the Dallas Museum of Art, Los Angeles County Museum of Art, and Smithsonian American Art Museum in Washington, D.C., among other institutions. Flack’s personal papers, meanwhile, will find their home at the Smithsonian’s Archives of American Art.
And Flack was recognized by H.W. Janson’s History of Art, where she was one of the first women artists added to the authoritative art history textbook when it published a third edition in 1986.
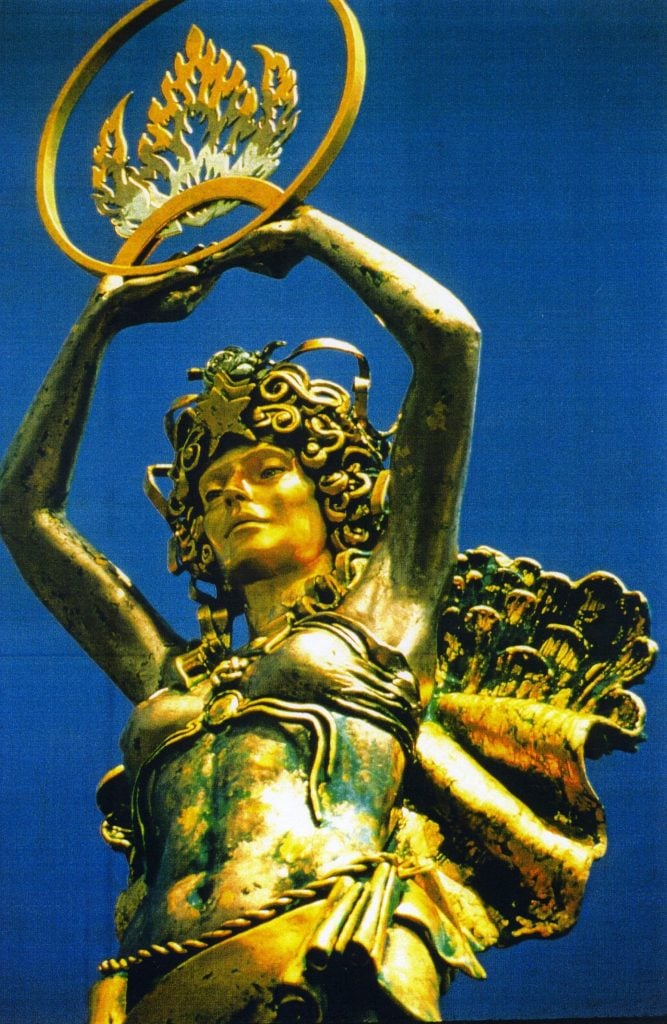

Audrey Flack, Civitas: Four Visions (1991), in Rock Hill, South Carolina. Photo courtesy of Hollis Taggart, New York.
By that time, Flack had left Photorealism behind to break new artistic ground, moving into large-scale bronze sculpture depicting female goddesses. This reinvention led to prominent public art commissions across the U.S., including Civitas (1991), a gateway monument in Rock Hill, South Carolina.
“Flack is one of a group of early feminist artists whose work was crucial in generating new ideas concerning the representation of women, and her goddesses continue to chart new territory,” Patricia Mathews wrote in Art in America in 1994.
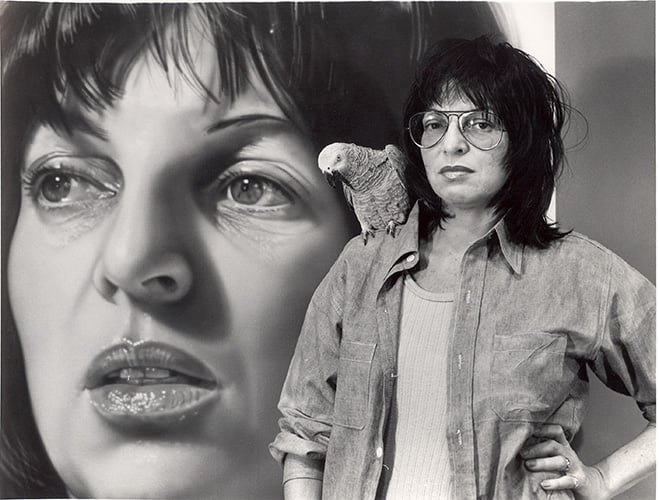

Audrey Flack and parrot with Self Portrait (1974). Photo courtesy of Louis K. Meisel Gallery, New York.
Recent years saw Flack return to painting, in what she dubbed her “Post-Pop Baroque” period. She remained active in the studio, and in October, the Parrish Museum of Art in Water Mill, New York, will present work from the last four years in “Audrey Flack NOW.”
“When I’m painting now, everything is at my fingertips. It’s magical,” Flack told Vogue this spring. “They say before you die you see everything from your life. In my 92 years, a lot pops up.”
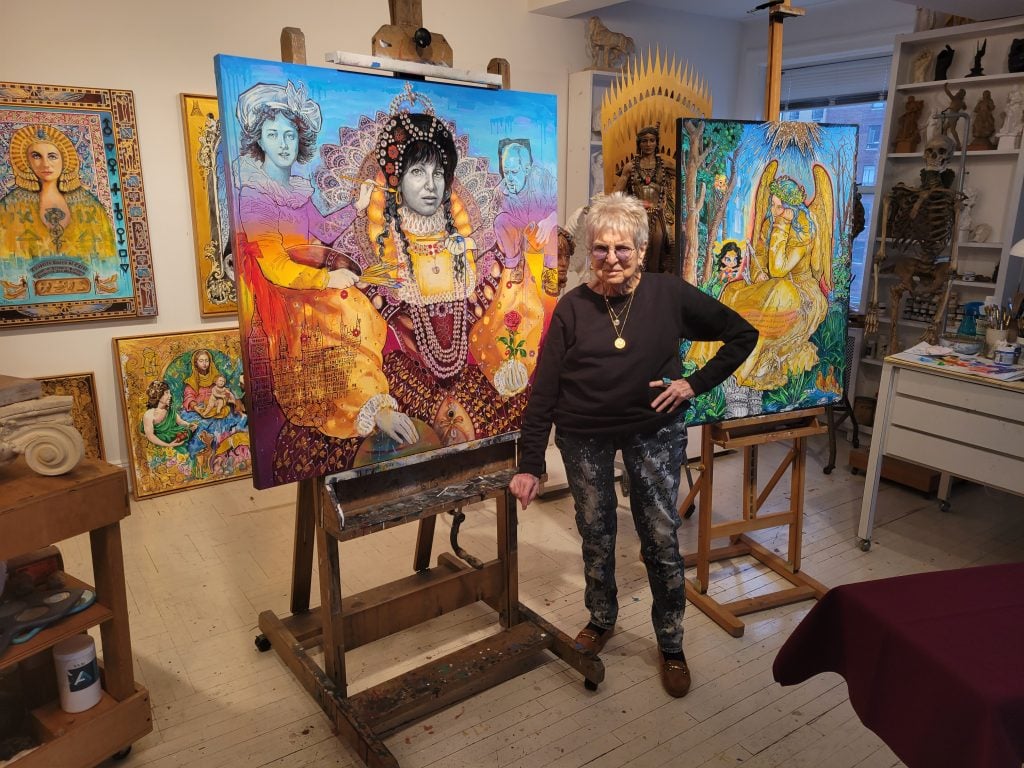

Audrey Flack in her studio January 2024. Photo courtesy of Hollis Taggart, New York.
This year saw Flack publish a deeply personal memoir, With Darkness Came Stars, detailing the artist’s abuse at the hands of her first husband, and the challenges of raising a nonverbal daughter with autism.
Flack is survived by her two daughters from her first marriage, Melissa and Hannah, and stepchildren Mitchell and Leslie. After her first marriage ended in divorce, Flack married her high school sweetheart, Robert Marcus, who died this May.
“Audrey Flack NOW” will be on view at the Parrish Museum of Art, 279 Montauk Highway, Water Mill, New York, October 13, 2024–April 6, 2025.
Follow Artnet News on Facebook:
References: this article is based on content originally published by Sarah Cascone on Artnet. You can read the full article here.